ใช้ Regression หาปัจจัยที่ส่งผลต่อตัวแปรตามมากที่สุด
หัวข้อในบทความนี้ได้แก่
มีงานวิจัยหลายงานที่ศึกษาเกี่ยวกับ “ผลกระทบที่ผลต่อ …” หรือ “ปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อ …” ซึ่งก็มักจะมีข้อมูลตัวแปรต้นอยู่หลายตัวแปร (xᵢ) และข้อมูลตัวแปรตามอยู่ 1 ตัว (y)
เราสามารถใช้ “regression” ในการอธิบายว่าตัวแปรต้น หรือ ปัจจัย (factor) แต่ละตัว มีความสัมพันธ์ (correlation) กับตัวแปรตามมากน้อยเพียงใด โดยค่าที่ใช้วัดคือ สัมประสิทธิ์สหสัมพันธ์ (correlation coefficient) ซึ่งโดยทั่วไปมีค่าอยู่ในช่วง [-1, 1]
correlation coefficient มีอยู่หลายประเภท โดยทั่วไปมักใช้ pearson correlation coefficient แต่ในที่นี้ผมจะใช้ “coefficient of determination” เพราะโฟกัสเฉพาะระยะห่างระหว่างตัวแปร 2 ตัวมากกว่า
1. Coefficient of Determination (ค่าสัมประสิทธิ์การตัดสินใจ)
หรืออีกชื่อนึงคือ R squared มีสูตรคือ




R²: coefficient of determination
SSᵣₑₛ: residual sum of squares คือ square error หรือ ค่าความคลาดเคลื่อนระหว่างค่าจริง (yᵢ) กับค่าที่ทำนาย (yᵢ^) กำลังสอง โดยค่า yᵢ^ จะแตกต่างกันตาม regression ที่เลือกใช้
SSₜₒₜ: ผลรวมความแปรปรวน (variance)
2. Regression แต่ละประเภท
จากสมการหา R² ด้านบน, yᵢ^ เป็นค่าจาก regression model ที่ใช้ในการหาความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างตัวแปร ตัวอย่างเช่น
2.1 Linear Regression

y = β₀ + β₁x₁ + β₂x₂ + … + βₙxₙ 2.2 Logarithmic Regression

y = β₀ + β₁ln(x₁) + β₂ln(x₂) + … + βₙln(xₙ) 2.3 Quadratic Regression

y = α₁x₁² + α₂x₂² + … + αₙxₙ² + β₁x₁ + β₂x₂ + … + βₙxₙ + γ2.4 Exponential Regression

y = β₀exp{β₁x₁ + β₂x₂ + … + βₙxₙ}y: ตัวแปรตาม
xᵢ: ตัวแปรอิสระ
β₀, γ: ค่า y เมื่อ xᵢ=0 (intercept)
αᵢ, βᵢ: ค่าสัมประสิทธิ์ของ xᵢ
นอกจากนี้ทุกสมการข้างต้นยังสามารถเพิ่มค่า error หรือ residual term +ϵ เข้าไปต่อท้ายได้ได้รูป
y = f(x₁, x₂, …, xₙ) +ϵซึ่ง ϵ หมายถึงผลต่างระหว่างค่าจริง (y) กับค่าที่ทำนาย (y^) แต่เพราะว่าต้องนำ error นี้ไปคำนวณ SSᵣₑₛ ดังนั้นจะไม่พิจารณา ϵ
3. ตัวอย่างการใช้งาน
ตัวอย่างการทำนี้ใช้ข้อมูล Crop yield Prediction จาก Kaggle

มีขั้นตอนย่อยได้แก่
3.2 ใช้ regression แต่ละชนิดหา coefficient of determination ของแต่ละตัวแปร
3.3 เปรียบเทียบค่า R² เพื่อหาปัจจัยที่ส่งผลต่อตัวแปรตามมากที่สุด
3.1 เตรียมข้อมูล
นำไฟล์ “crop yield data sheet.xlsx” มาวิเคราะห์ ใช้ pandas อ่านตัวอย่างข้อมูลในไฟล์ได้
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_excel("crop yield data sheet.xlsx")
df.sample(5)
ตรวจสอบหน้าตาข้อมูล พบว่าข้อมูลมีทั้งหมด 109 row, 7 column
df.info()
เพราะว่ามีข้อมูลทั้งหมด 109 row, 7 column แต่แต่ละ column มีข้อมูลที่ไม่ใช่ null อยู่ 99 หรือ 100 row แสดงแถวที่มีค่า null ออกมาได้
null_data = df[df.isnull().any(axis=1)]
null_data
เพราะว่าแถวที่มี null ข้อมูลขาดหายไปทั้งหมด ดังนั้นตัดแถวเหล่านั้นออกไปเลย ได้
df = df.dropna()
df.shapeผลลัพธ์คือ (99, 7) หมายถึง 99 row, 7 column เพราะเราเอา row ที่มีค่า null ออกไป 10 row
กำหนดให้ “Rain Fall (mm)”, “Fertilizer”, “Temperatue”, “Nitrogen (N)”, “Phosphorus (P)”, “Potassium (K)” คือตัวแปรอิสระ x₁, x₂, x₃, ,x₄, x₅, ,x₆ ตามลำดับ และ “Yeild (Q/acre)” คือตัวแปรตาม y ได้
x1 = df["Rain Fall (mm)"]
x2 = df["Fertilizer"]
x3 = df["Temperatue"]
x4 = df["Nitrogen (N)"]
x5 = df["Phosphorus (P)"]
x6 = df["Potassium (K)"]
y = df["Yeild (Q/acre)"]3.2 ใช้ regression แต่ละชนิดหา coefficient of determination ของแต่ละตัวแปร
ผมใช้ np.polyfit ในการสร้าง regression แต่ละแบบ และ matplotlib.pyplot ในการสร้างกราฟออกมา
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltเพราะว่าต้องการหาว่า xᵢ ตัวไหนส่งผลต่อ y มากที่สุด ดังนั้นแบ่งตามประเภท regression และดูว่าในแต่ละ regression xᵢ ส่งผลต่อ y มากที่สุด
1. Linear Regression
parameter ที่ใช้ใน np.polyfit ได้แก่ ค่า x, y, และเลขชี้กำลังสูงสุด (degree) ของ x ดังนั้นในกรณีของ x₁ เขียนออกมาได้
fit = np.polyfit(x1, y, 1)
fitได้ผลลัพธ์คือ array([4.35755293e-03, 5.34746538e+00]) โดยตัวแรกคือสัมประสิทธิ์ของ x และตัวสุดท้ายคือ intercept ดังนั้น ได้ y^ คือ
y_pred = fit[0]*x1 + fit[1]สร้างกราฟแสดง y จริง, y^ และเส้น linear regression ได้
plt.scatter(x1, y, label="Truth values")
plt.scatter(x1, y_pred, c="red", label="Predicted values")
x_line = np.arange(np.min(x1), np.max(x1))
y_line = fit[0]*x_line + fit[1]
plt.plot(x_line, y_line, c="red")
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
การหา R² ผมใช้ sklearn.metrics.r2_score ดังนั้นเขียนออกมาได้
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
r2 = r2_score(y, y_pred)
r2ได้ผลลัพธ์คือ 0.7862747305187001 คือค่า R² ของ x₁ เมื่อเทียบกับ linear regression
สามารเขียน function เพื่อสร้าง linear regression, สร้างกราฟ และหาค่า R² จาก xᵢ คือ
x = [x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6]
def line_regress(x, y):
r2 = []
row = (len(x)+2) // 3 # แต้ละ row มี 3 column
fig, axs = plt.subplots(row, 3, figsize = (15, 10))
for i in range(len(x)):
r = i // 3
c = i % 3
xi = np.array(x[i], dtype=float)
fit = np.polyfit(xi, y, 1)
y_pred = fit[0]*xi + fit[1]
x_line = np.arange(np.min(xi), np.max(xi+1))
y_line = fit[0]*x_line + fit[1]
r2_value = r2_score(y, y_pred)
r2.append(r2_value)
axs[r, c].scatter(xi, y, label="Truth values")
axs[r, c].scatter(xi, y_pred, c="red", label="Predicted values")
axs[r, c].plot(x_line, y_line, c="red")
axs[r, c].set_xlabel(f"x{i}")
axs[r, c].set_ylabel('y')
axs[r, c].legend()
axs[r, c].set_title(f"x{i}: R squared = {r2_value:.2f}", fontweight='bold')
fig.suptitle("Linear Regression", fontsize=25, fontweight='bold')
plt.show()
return r2
line_regress(x, y)
2. Logarithmic Regression
คล้ายกับ linear regression แต่ xᵢ ที่เอาไปเข้า model คือค่า ln(xᵢ) เช่นของ x₁ เขียนออกมาได้
log_x1 = np.log(x1)
fit = np.polyfit(log_x1, y, 1)
y_pred = fit[0]*np.log(x) + fit[1]function ที่ใช้สร้างคล้ายกับของ linear regression แค่เปลี่ยน ส่วนที่ใช้หา y_pred กับเส้นกราฟเปรียบเทียบ
def log_regress(x, y):
r2 = []
row = (len(x)+2) // 3
fig, axs = plt.subplots(row, 3, figsize = (15, 10))
for i in range(len(x)):
r = i // 3
c = i % 3
xi = np.array(x[i], dtype=float)
log_xi = np.log(xi)
fit = np.polyfit(log_xi, y, 1)
y_pred = fit[0]*log_xi + fit[1]
x_line = np.arange(np.min(xi), np.max(xi+1))
y_line = fit[0]*np.log(x_line) + fit[1]
r2_value = r2_score(y, y_pred)
r2.append(r2_value)
axs[r, c].scatter(xi, y, label="Truth values")
axs[r, c].scatter(xi, y_pred, c="red", label="Predicted values")
axs[r, c].plot(x_line, y_line, c="red")
axs[r, c].set_xlabel(f"x{i}")
axs[r, c].set_ylabel('y')
axs[r, c].legend()
axs[r, c].set_title(f"x{i}: R squared = {r2_value:.2f}", fontweight='bold')
fig.suptitle("Logarithmic Regression", fontsize=25, fontweight='bold')
plt.show()
return r2
log_regress(x, y)
3. Quadratic Regression
ที่ np.polyfit กำหนด degree=2 กรณีของ x₁ เขียนออกมาได้
fit = np.polyfit(x1, y, 2)
y_pred = fit[0]*x1**2 + fit[1]*x1 + fit[2]สร้างกราฟของแต่ละ xᵢ ได้

4. Exponential Regression
คล้ายกับ logarithmic regression แต่ ค่าที่อยู่ใน ln คือ y ได้
ln(y) = β₀ + β₁x₁
∴ y = exp{β₀ + β₁x₁} = γexp{β₁x₁} ; γ=exp{β₀} มอง γ เป็นค่าคงที่ดังนั้นกรณีของ x₁ เขียนออกมาได้
fit = np.polyfit(x1, np.log(y), 1)
y_pred = np.exp(fit[0]*x1 + fit[1])สร้างกราฟของแต่ละ xᵢ ได้

3.3 เปรียบเทียบค่า R² เพื่อหาปัจจัยที่ส่งผลต่อตัวแปรตามมากที่สุด
สร้างตารางเปรียบเทียบค่า R² ของแต่ละตัวแปรต้นออกมาได้

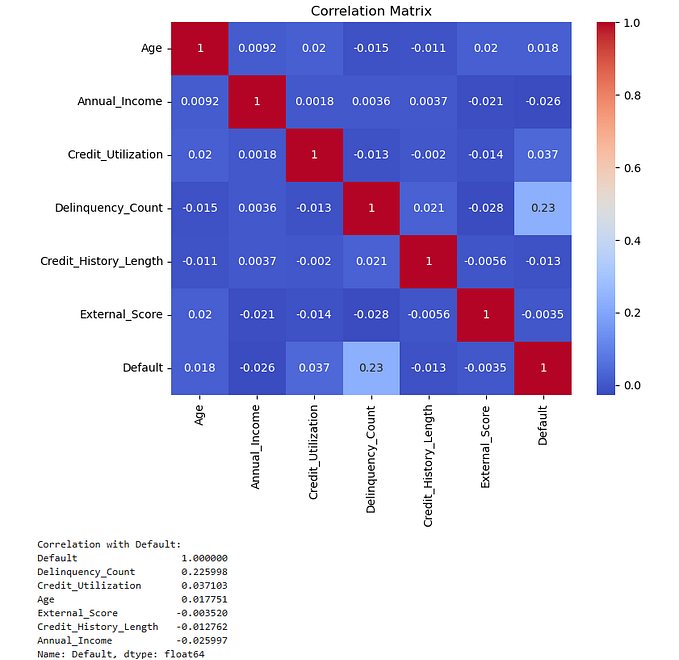
เพราะฉะนั้นจากข้อมูลสรุปได้ว่าอุณหภูมิส่งผลต่อปริมาณผลผลิตมากที่สุด